It’s important to eat a range of nutritious foods throughout your pregnancy, but there are some foods that you’re advised to either limit or avoid. This is mainly due to certain foods increasing your risk of food poisoning. So in this blog we’ll explore the foods you need to both limit and avoid, to help keep you and your baby safe and healthy.
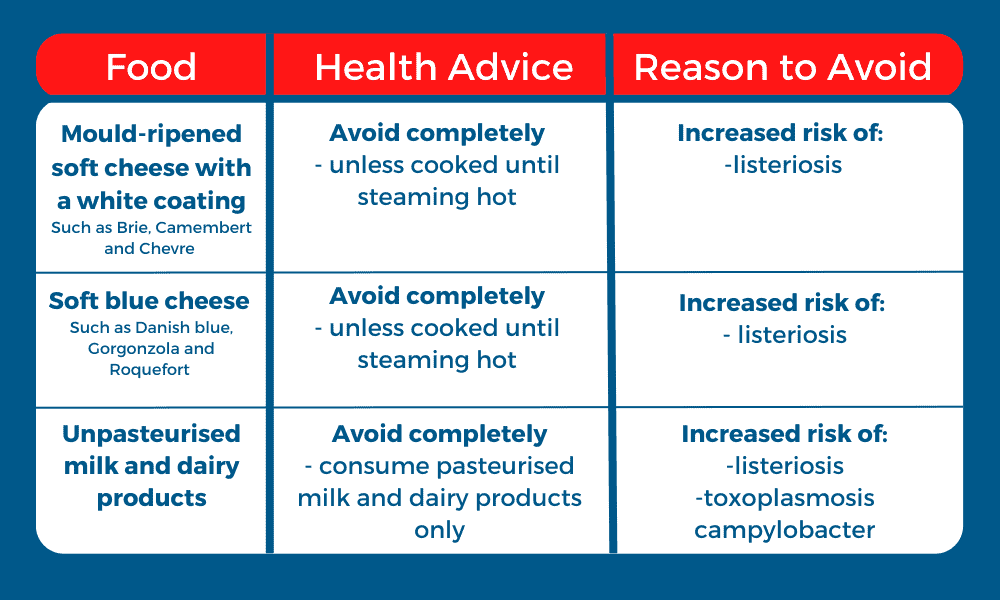
Dairy foods to avoid during pregnancy, include:

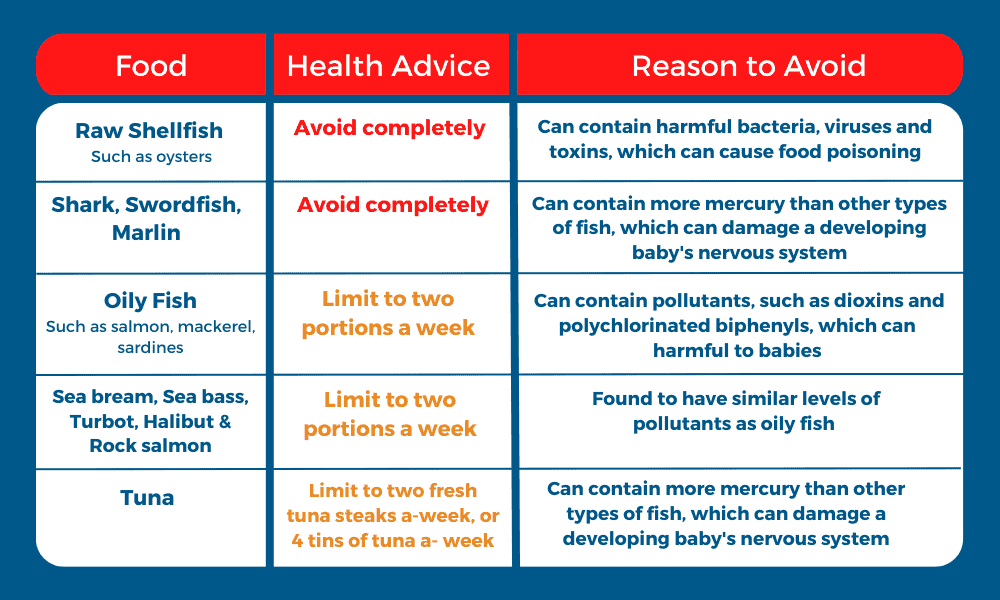
Fish to limit and avoid during pregnancy, include:

A note on smoked fish
Due to a listeria outbreak linked to smoked fish, people at higher risk of serious infection (including people who are pregnant) should only eat smoked fish products that have been thoroughly cooked. It is currently advised that when cooking smoked fish products (e.g. smoked salmon or trout) at home, make sure they are steaming hot all the way through.
You can find additional information on the NHS (opens in new tab) and the Food Standards Agency (opens in new tab).
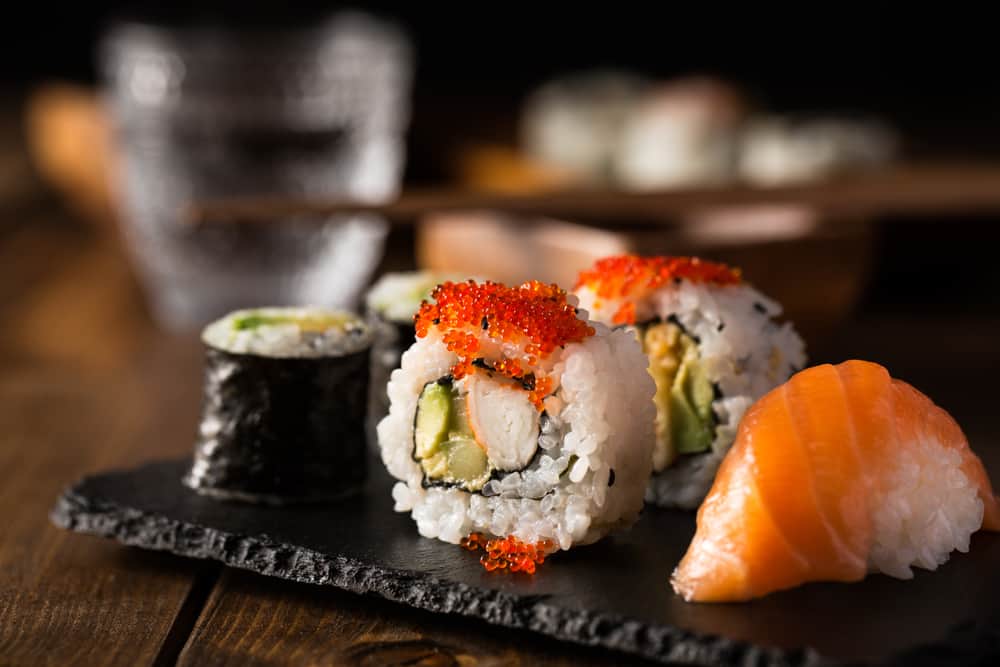
What about sushi?
It’s usually safe to eat sushi in pregnancy, but it does depend on what fish the sushi is made from:
Raw fish made sushi:
- Occasionally, raw fish like salmon contains small parasitic worms, such as anisakis
- These worms can cause health problems if eaten raw or in undercooked fish infected with them
- Freezing raw wild fish kills any worms that may be present and makes it safe to eat
- Certain farmed fish, destined to be eaten raw in dishes like sushi, such as farmed salmon, no longer need to be frozen beforehand. This is because these particular types of farmed fish are very unlikely to contain parasitic worms because of the rearing methods used.

Cured fish made sushi:
- Some fish used to make sushi, such as smoked salmon, doesn’t need to be frozen before it’s used because most smoking processes kill any parasitic worms in the fish.
- Other methods, such as salting or pickling, also make raw fish safe to eat.
Shellfish made sushi:
- A lot of sushi contains shellfish
- It’s recommended that pregnant women should only eat cooked shellfish. Raw shellfish can contain harmful viruses and bacteria that can cause food poisoning.
Sushi in restaurants:
- If you want to eat sushi in a restaurant, it’s always best to ask how it’s been prepared, so you can see if it’s safe for you to have.
Homemade sushi:
- If making home-made sushi-, with fresh fish, make sure to freeze the fish for at least 4 days before using it.
A note if you’ve breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed:
It’s recommended that you have no more than:
- one portion of either swordfish, marlin and shark each week due to their high levels of mercury
- two portions of oily fish each week as they contains pollutants.

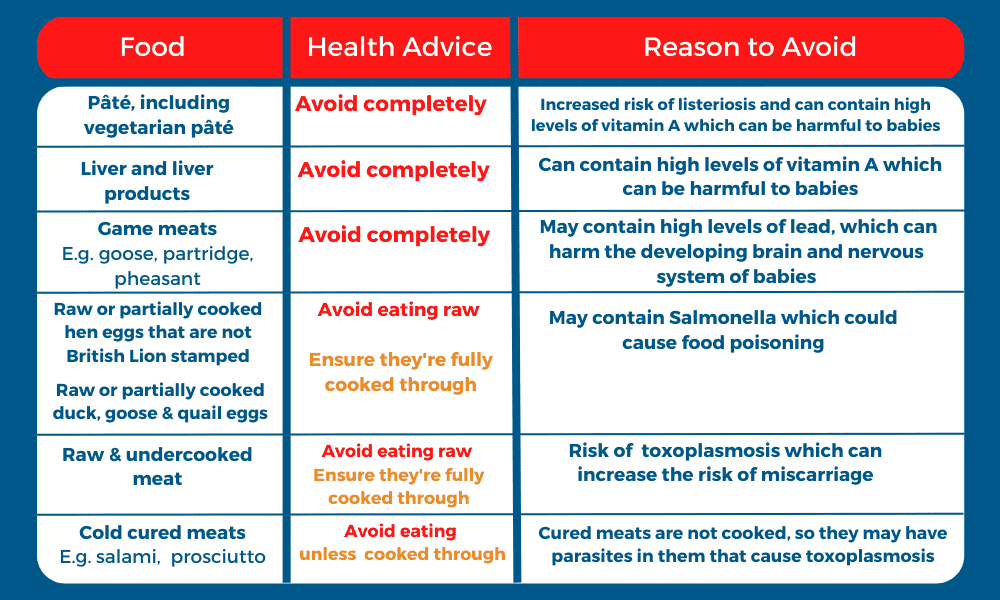
Other proteins foods to avoid during pregnancy, include:
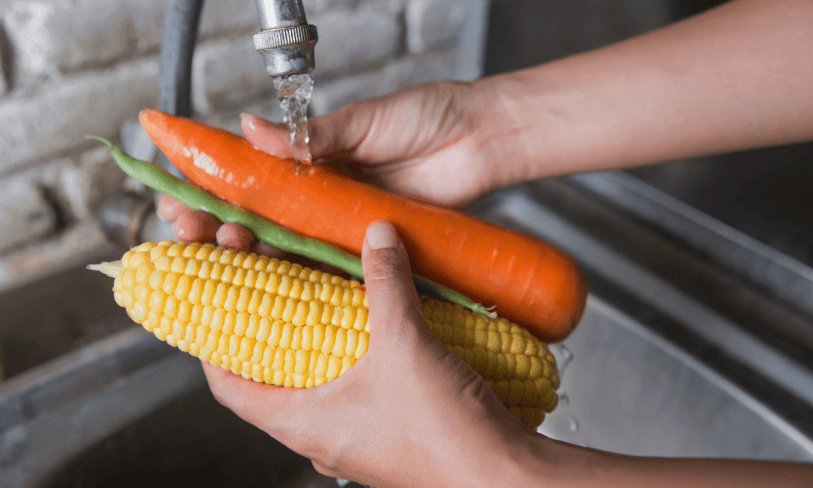
Unwashed fruits, vegetables and salads
Unwashed fruits, vegetables and salads can have soil on them. Most of the bacteria will be in the soil attached to the produce. Washing will help remove bacteria, including E.coli, from the surface of them. Washing loose produce is particularly important as it tends to have more soil attached to it than pre-packaged fruit and vegetables.
When you wash vegetables, wash them under a running tap and rub off the soil and dirt.
For more information, visit the NHS website (opens in new tab).

Liquorice Root
While liquorice is safe to eat, liquorice root should be avoided as it contains high levels of glycyrrhizin.

Caffeine
Hot drinks, such as tea and coffee, can contribute to your fluid intake. However, it’s important to limit your caffeine intake to 200mg per day, as having more than this can increase the risk of miscarriage or having a low birth weight baby. This is also the advice if you’re breastfeeding.
Let’s take a look at the caffeine content of these common drinks and foods:

So as you can see, two cups of instant coffee would bring you to the maximum recommendation of 200mg of caffeine a day.
It might not always be obvious that drinks and foods contain caffeine either, so it’s a good idea to check food labels so you can keep a check on the amount that you’re having.
The following foods and drinks can also contain caffeine:
- Green tea
- Cocoa beans and chocolate, including some hot chocolates
- Coffee-containing foods, such as coffee flavour ice cream and frozen yoghurt
- Some chewing gums
- Some fizzy drinks, such as cola
- Energy drinks.
It’s also best to avoid herbal teas, except for those made with ingredients that would be a normal part of the diet, such as mint, peppermint, lemon. The NHS also recommend no more than 4 cups of herbal tea a- day and encourage you to opt for a variety of different teas so you’re not having too much of any one kind.

A note if your breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed:
Caffeine is a stimulant and can pass through your breast milk and make your baby restless. It’s therefore a good idea to cut caffeine out while breastfeeding , however, if you do drink caffeine, try to have less than 200mg a day.
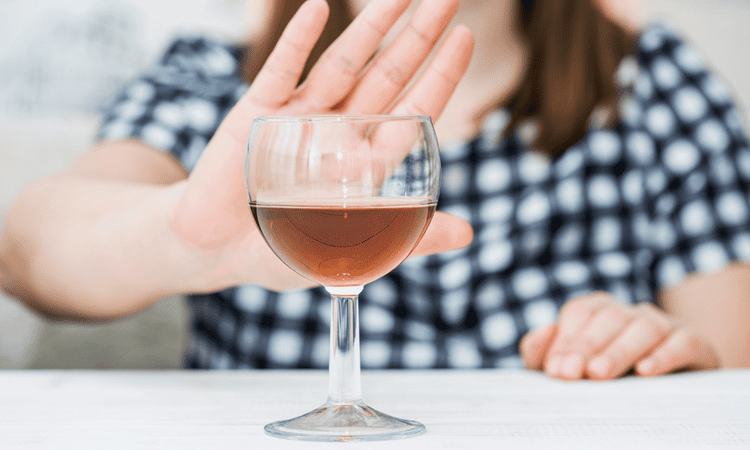
Alcohol
It’s recommended that you avoid alcohol as there are no known safe levels for drinking during pregnancy.
This is especially important during the first 3 months of pregnancy (the first trimester), when your baby is growing and developing quickly.
Drinking alcohol at any stage of pregnancy has been linked to complications, such as miscarriage, premature birth and low birth-weight.
If you drink heavily or you’re having trouble stopping, speak to your GP or midwife. They will be able to give you specialist advice and support.
For more information and links to support services, visit the NHS website (opens in new tab).

A note if you’re breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed:
When you’re breastfeeding, the safest approach is to avoid drinking alcohol. While the occasional drink is unlikely to harm your breastfed baby, if you choose to consume alcohol, it’s recommended that you have no more than 1 or 2 units once or twice a week
If you’d like more information on alcohol and breastfeeding, visit the Start4Life (opens in new tab) website here.
Eating Well During Pregnancy Online Course
You can also find additional information on how to eat well during your pregnancy, by signing up to our FREE online course here (opens in new tab).

You can also check out our blog ‘How to Eat Well During your Pregnancy (opens in new tab)‘.

This informative blog post on foods to avoid in pregnancy is a valuable resource for expectant mothers. It offers important insights into potential food risks and provides guidance on maintaining a healthy diet during pregnancy. Thank you, Early Start Group, for sharing these helpful recommendations!